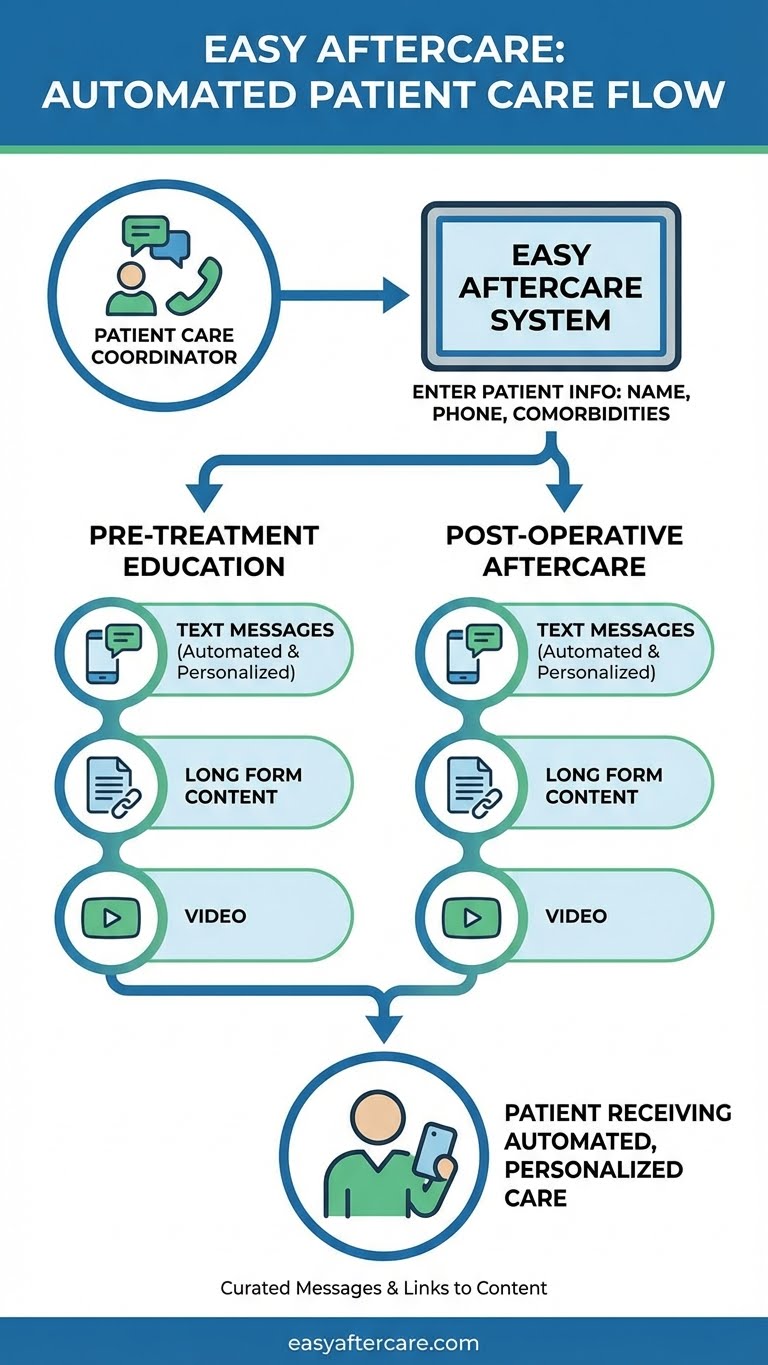
Clinical Outcomes & Safety Studies
Readmission & ED Reduction (Post-Discharge Texting): A March 2024 study of a large hospital texting program found engaged patients used significantly fewer 30-day acute-care resources, including 29% fewer readmissions, 20% fewer revisits (and were 23% less likely to revisit), and were 27% less likely to be readmitted.
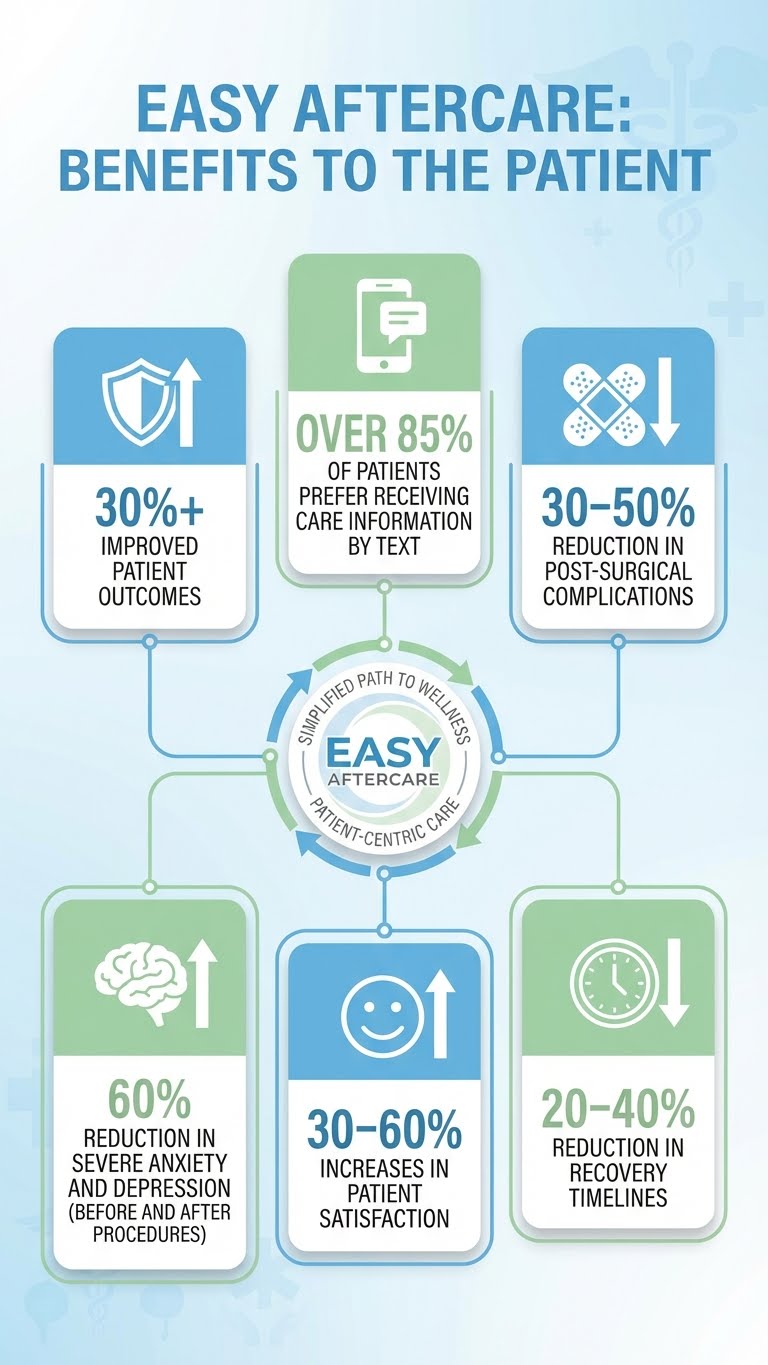
Laparoscopic & Abdominal Surgery (Education Impact): A 2024 systematic review of 17 studies found 88% reported statistically significant postoperative improvements, with educational videos showing strong impact on reducing anxiety, nausea, and pain. A separate 2024 review found group digital education led to a 0.7-day reduction in length of stay and nearly halved the odds of complications in abdominal surgery.
Virtual Transition Clinics (Readmissions): A study published in 2025 reported 30-day readmissions of 14.9% in a hospitalist-led virtual transition clinic group vs 20.1% with standard care.
Remote Monitoring & Digital Follow-Up (Post-Op Outcomes)
Total Hip/Knee Arthroplasty (App-Based Monitoring): A 2024 study found app-enrolled patients had statistically lower length of stay and fewer ED visits; patients not enrolled had 2.31× greater odds of an ED visit within 60 days post-surgery (no significant difference in readmissions in that study).
Orthopedic Surgery (Digital Messaging vs Standard Communication): A 2024 randomized controlled trial reported patient-initiated phone calls dropped from a mean of 2.3 to 0.5 calls (control vs intervention) within 14 days post-op, alongside improved patient satisfaction with access after discharge.
Patient-Reported Operational Impact (Large Health System Deployment): In one health-system implementation report, patients reported 39% avoided one or more phone calls to the care team and 13% avoided at least one ED visit after receiving a structured digital care journey.
Patient Engagement & Satisfaction Research
HCAHPS & Experience Scores (Texting Engagement): The March 2024 post-discharge texting study found the engaged cohort had higher HCAHPS scores in all domains than non-engaged patients.
Smartphone-Delivered Education & Adherence (Systematic Review): A JMIR review concluded that delivering timely medical information via smartphones/tablets improved patient knowledge, adherence, satisfaction, and clinical outcomes, with stronger effects in shorter, higher-frequency interventions.
Mental Health Outcomes (Severe Anxiety & Depression)
Pre- and Post-Op Anxiety and Depression: Almarshad et al., 2022 (early postoperative period cohort): Using PHQ-9 ≥10, preoperative depression was 9.2% and depression within 5 days post-op was 32.0%; using STAI-S ≥40, pre-op anxiety was 47.7% and post-op anxiety was 72.8%.
Post-Op Depression in Cosmetic Surgery: 30% of patients experienced a postoperative depressive reaction after facelift surgery.
Digital Mental Health Program (Severe Symptoms): A 2023 retrospective analysis reported that participants with severe baseline anxiety/depression experienced clinically significant improvement after 6 months—approximately ~9 points improvement in anxiety and ~12 points improvement in depression scores with sustained engagement.
Telepsychiatry Outcomes (Depression & Anxiety): A 2023 outpatient telepsychiatry analysis reported mean score changes of –6.71 (GAD-7) and –6.85 (PHQ-8), with ~45.7% reduction in anxiety scores and ~43.1% reduction in depression scores among those with at least moderate symptoms at baseline.
Perioperative Stress Reduction (LOS + Well-Being): A 2025 perioperative digital intervention study reported the intervention group spent 17.12% fewer days in the hospital and demonstrated improvements across psychological dimensions linked to stress and negative emotions.
Digital CBT for Generalized Anxiety Disorder (RCT): A 2025 randomized clinical trial (n=351) found a smartphone-delivered digital CBT program achieved greater anxiety reduction and higher remission rates than an active psychoeducation control.
Economic & Operational Impact Studies
Education Time Burden Reduction: A classic review found computer-based patient education reduced time required for learning by as much as 40%, freeing clinician time for higher-risk or individualized instruction.
Reducing Post-Op Calls (Operational Load): In addition to the 2024 orthopedic RCT (2.3 → 0.5 calls), patient-reported outcomes from a large health system digital pathway rollout indicate measurable reductions in outbound/inbound communication burden (e.g., 39% avoiding one or more calls).
Systematic Reviews & Protocols (2024–2025)
Digital Surgery Scheduling & Pre-Op Equity/Safety (Protocol): A 2025 systematic review protocol is evaluating how digital scheduling/education systems impact patient safety, timeliness, and equity.
Pediatric Post-Op Digital Interventions: A 2024 systematic review found mobile messaging interventions can improve parental knowledge and reduce anxiety and rehospitalization-related outcomes in pediatric post-op care contexts.
Group Pre-Op Education (Narrative/Systematic Review): A 2024 review found group-based digital education is associated with shorter length of stay and reduced complication odds in major elective surgery settings.
Malpractice Claims & Risk Exposure (Why Documentation + Comms Matter)
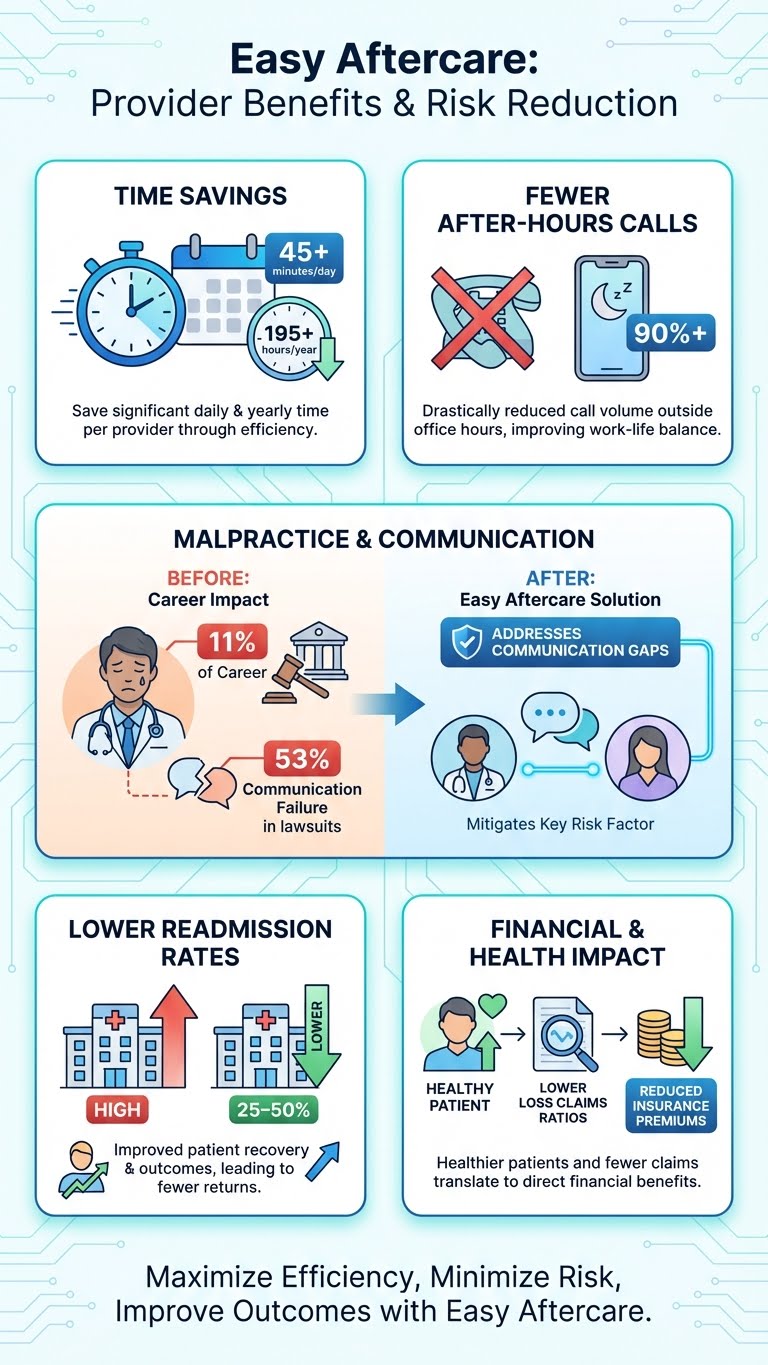
Time Cost of Malpractice Litigation: A large insurer dataset analysis found the average physician spends 50.7 months, nearly 11% of a 40-year career—with an unresolved malpractice claim.
How Common Claims Are + Typical Payments: A specialty-level analysis reported 7.4% of physicians face a malpractice claim each year and 1.6% have a claim that results in payment (i.e., most claims do not pay). Across specialties, the mean indemnity payment was $274,887 (median $111,749).
Concentration of Risk (Repeat Claimants): A major study found ~1% of physicians accounted for 32% of paid malpractice claims, meaning risk can cluster, and consistent patient education processes help reduce preventable exposure.
Communication Failure as a Root Cause (High-Leverage for Aftercare)
Communication Failures in Claims: A national claims database study found communication failures were identified in 49% of malpractice claims; among those, 53% involved provider-patient miscommunication and 47% involved provider-provider miscommunication.
Large-Scale CRICO Findings: CRICO Strategies reported communication failures were a factor in 30% of 23,658 malpractice cases filed over a multi-year period—underscoring why consistent, documented patient education and clear contingency planning matters.
Insurance Loss Ratios & Market Pressure (Why Premiums Rise)
Loss Ratio Pressure (Medical Professional Liability): AM Best reporting has tracked adjusted loss ratio levels for U.S. medical professional liability underwriters and shows loss ratio volatility (including periods where average adjusted loss ratios are in the ~50%+ range, with some writers exceeding 100%), reinforcing how claims experience drives underwriting scrutiny and rate pressure.
Premium Growth (Market Signal): AM Best reported total U.S. medical professional liability direct premiums written rose 5.4% to $13.02B in 2024, an indicator of sustained premium pressure in the market.
State-Level Loss/Defense Cost Ratios (Example – WA): Washington’s medical malpractice annual reporting has shown combined incurred loss + defense cost ratios commonly in the ~80%+ range in recent multi-year windows (illustrating how defense costs materially affect total claim economics).
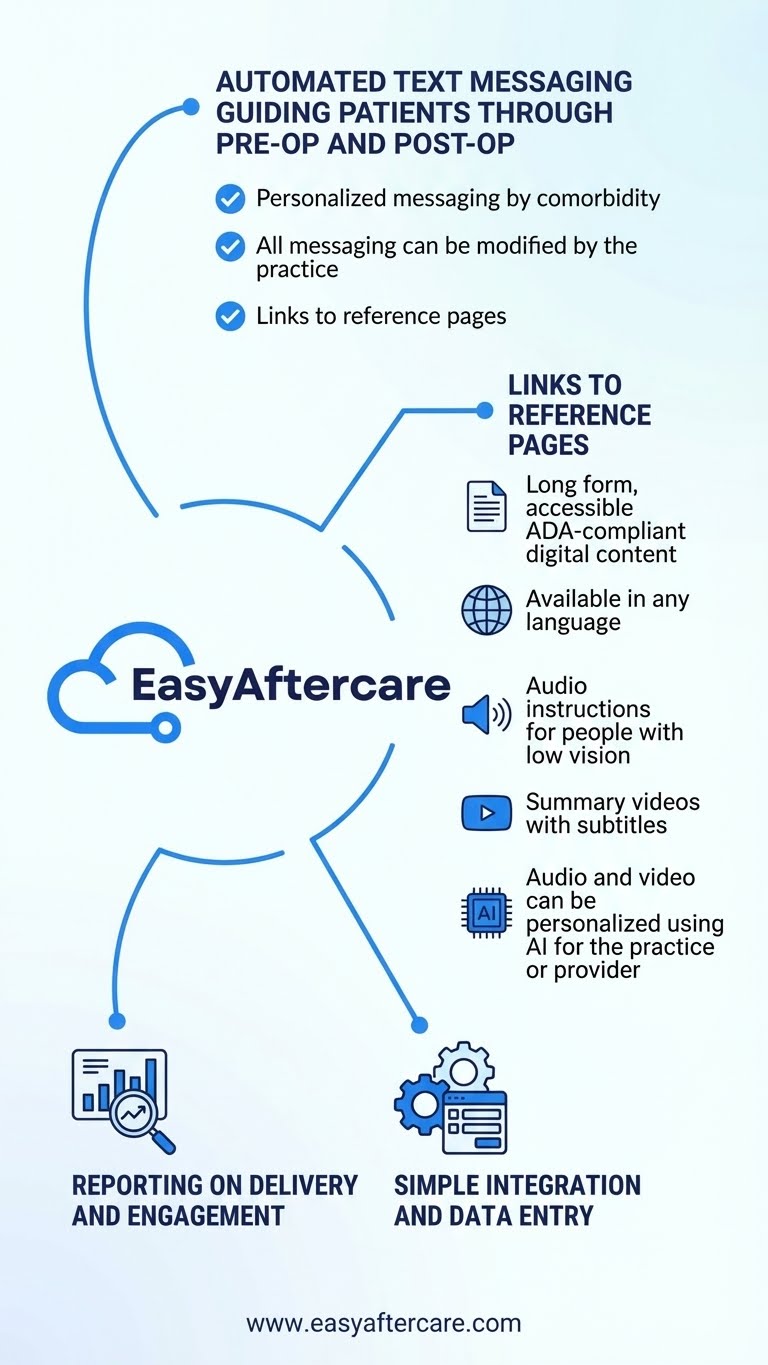
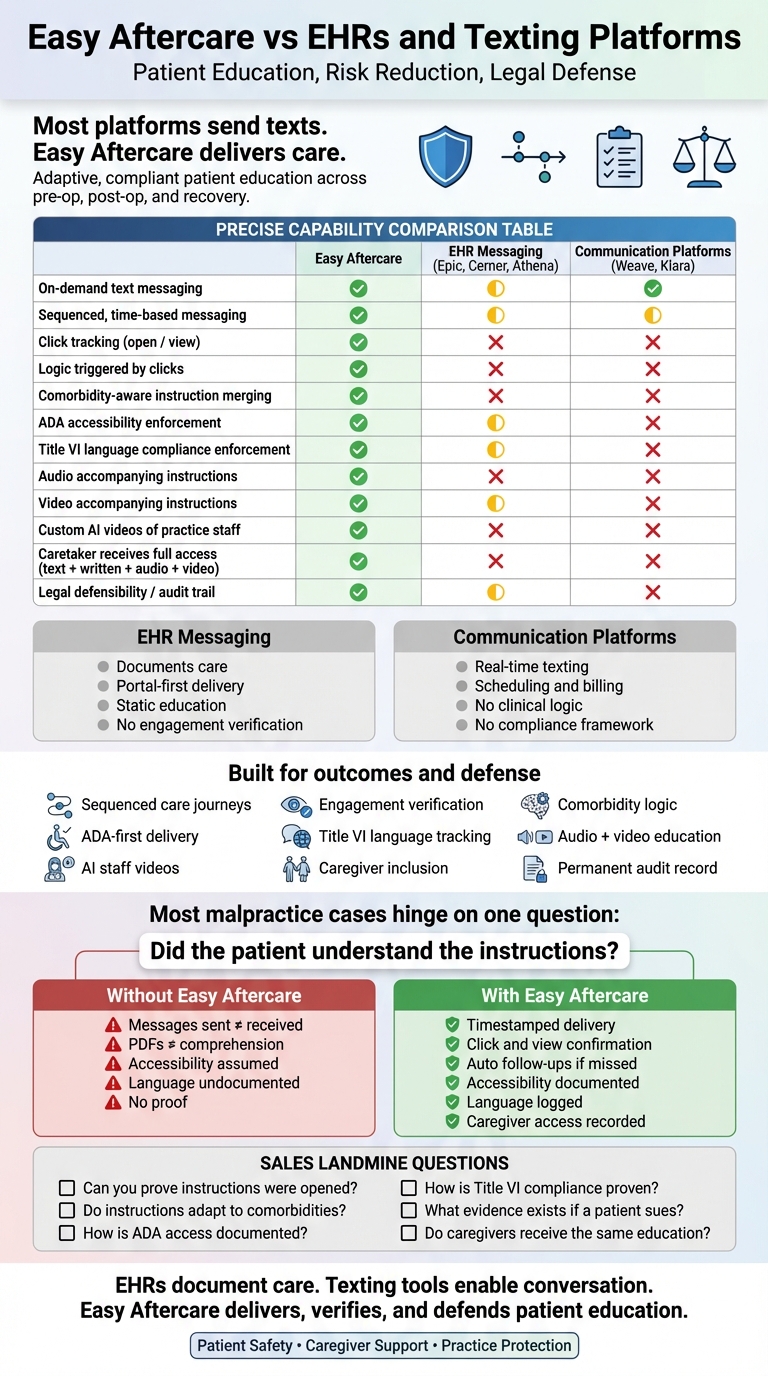
Digital Accessibility & ADA Compliance (Patient Education Must Be Accessible)
Most Websites Still Fail Basic Accessibility: The WebAIM Million (2024) found 95.9% of homepages had detectable WCAG failures, with 81.0% having low-contrast text and 54.5% missing alt text—exactly the kinds of issues that make patient education unusable for low vision and blind patients.
Healthcare Webpages Can Be Especially Problematic: A 2024 ophthalmology hospital webpage accessibility study found all assessed webpages had accessibility issues; color contrast issues appeared on 87% of sites evaluated.
ADA Web Lawsuit Volume (Risk Signal): UsableNet’s tracking indicates 4,187 digital accessibility lawsuits were filed by the end of 2024 (state + federal), showing that accessibility risk is active and growing.
ADA Effective Communication (Hearing/Vision Disabilities): DOJ guidance requires auxiliary aids/services when needed to communicate effectively - relevant to patient instructions for deaf/hard-of-hearing and blind/low-vision patients.
Language Access Compliance (Title VI – Civil Rights Act of 1964)
Meaningful Access for Limited English Proficiency (LEP): HHS OCR explains that Title VI (and related regulations) requires recipients of federal financial assistance to take reasonable steps to provide meaningful access to LEP persons—critical for delivering patient education in the patient’s language.
Canadian Accessibility Compliance (Accessible Canada Act – ACA)
Barrier-Free Canada by 2040: The Accessible Canada Act is a federal law aiming to identify, remove, and prevent barriers for people with disabilities, with a goal of a barrier-free Canada by 2040. Federally regulated entities have planning and reporting obligations, and accessible communication standards are a core theme.
Practice Growth & Retention (Business Case)
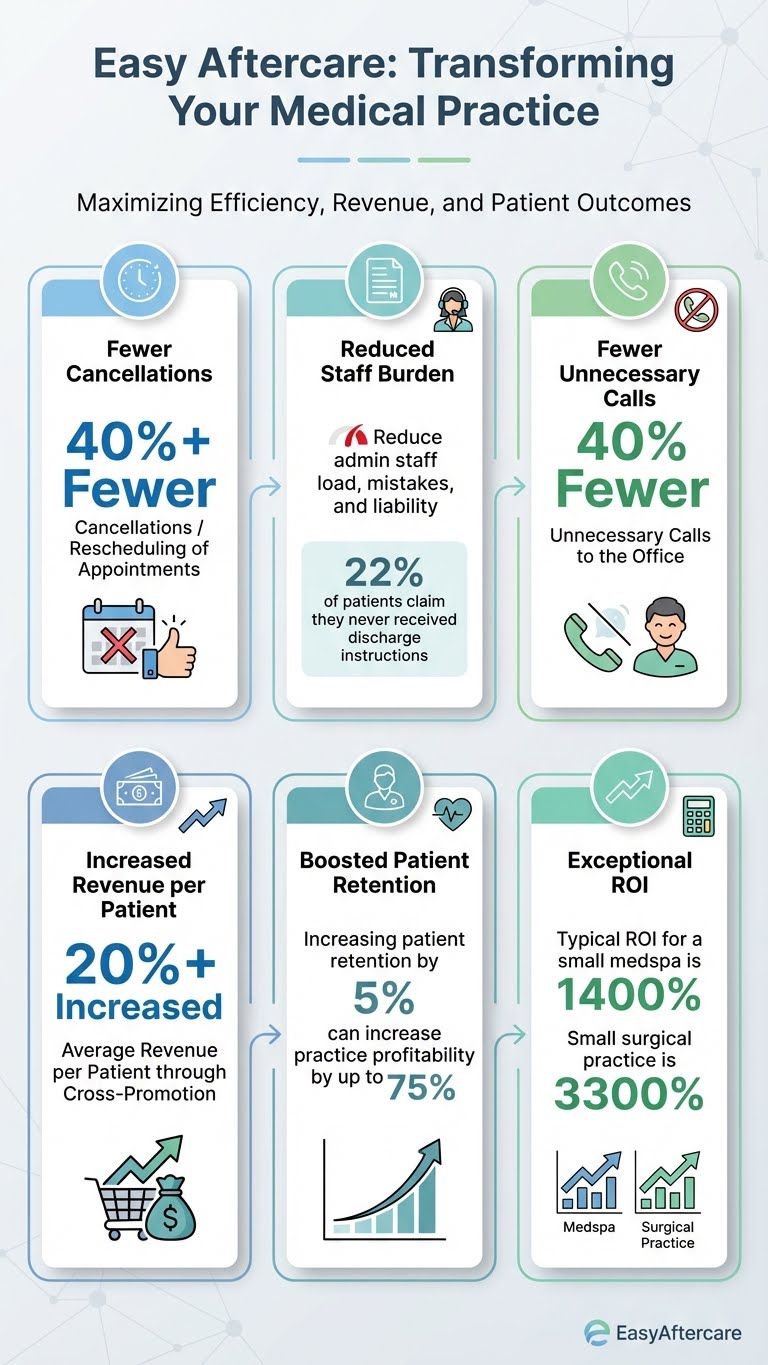
Retention Economics: Bain/HBR-cited research indicates increasing retention rates by 5% can increase profits by 25% to 95%. Better aftercare reduces complications, callbacks, and dissatisfaction—directly supporting retention and word-of-mouth growth.
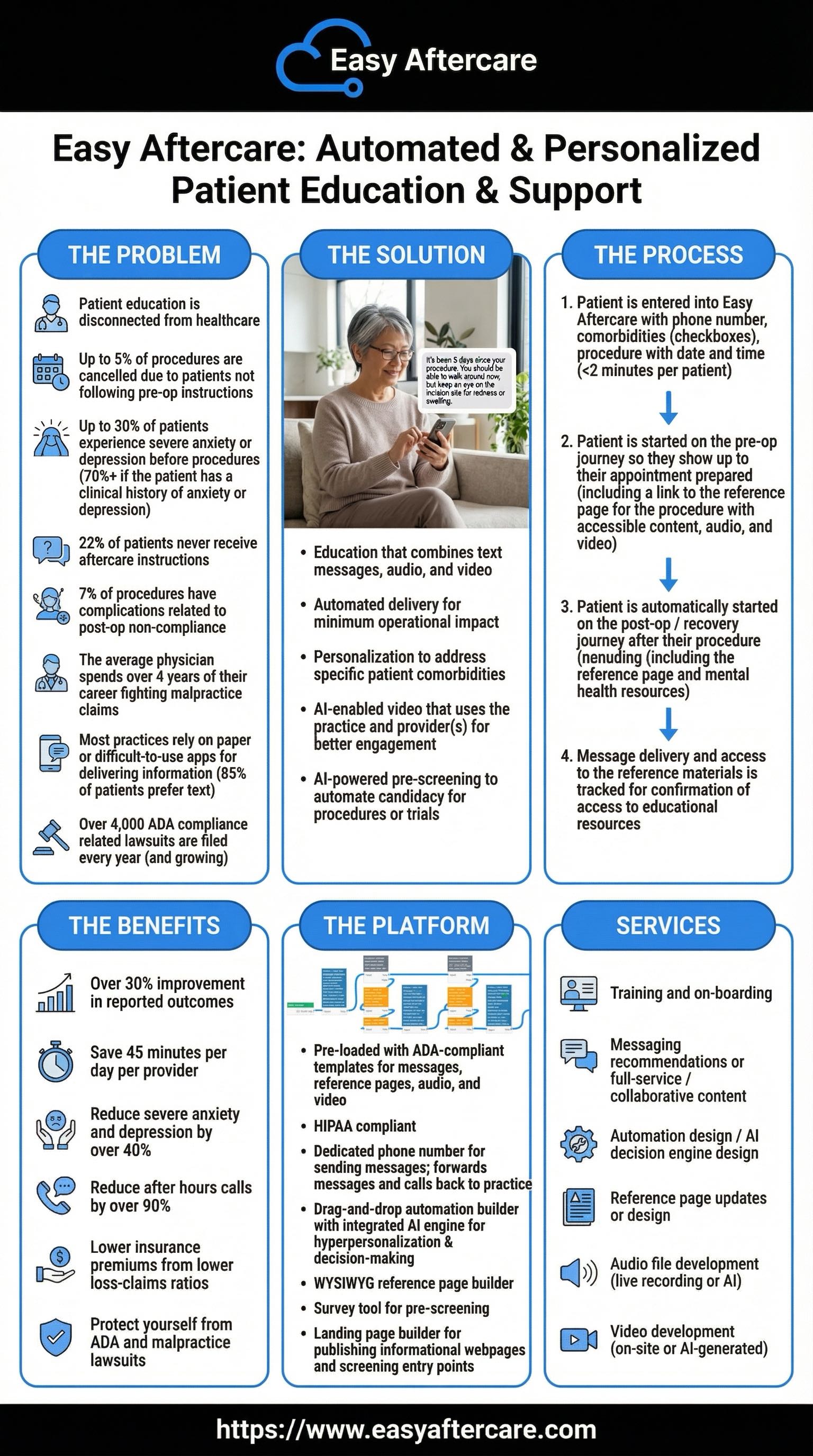
Patient Education Failures & Preventable Complications (U.S. & Western Systems)
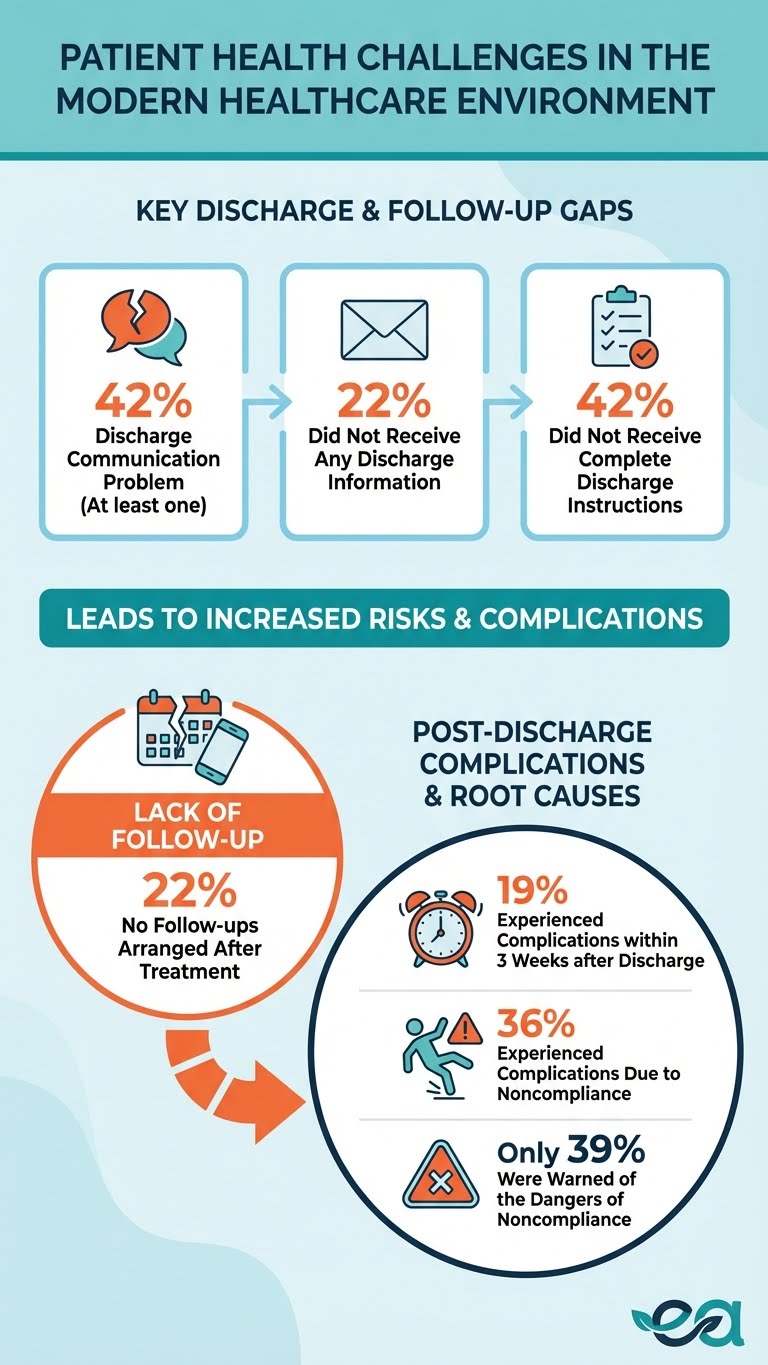
“No Aftercare Instructions” at Scale (High-Income Countries): In a 2025 analysis of an international health policy survey across 10 high-income nations, 42.5% of respondents reported at least one discharge communication problem; 22.2% reported they did not receive written discharge information, 22.8% reported no follow-ups were arranged, and 19.8% reported no discussion on medications.
Adverse Events After Discharge Are Common (U.S.): A prospective cohort study reported 19% of patients experienced an adverse event within ~3 weeks after discharge; events included a substantial burden of medication-related harm (adverse drug events were a leading category), with material portions considered preventable or ameliorable.
Patients Often Don’t Understand What to Do Next (ED Discharge): A study of emergency department discharge found 42% of patients did not receive complete discharge instructions; poor understanding ranged from 24% (follow-up plan) to 64% (return-to-ED instructions).
Medication “Knowledge Gaps” Are Extreme During Care (Inpatients): In a cross-sectional study of internal medicine inpatients, 96% omitted at least one prescribed hospital medication when asked to list what they were receiving, omitting an average of 6.8 medications; 44% believed they were receiving at least one medication that was not actually prescribed, and only 28% reported having seen their hospital medication list.
Complications Linked Directly to Noncompliance (Post-Op Instructions): A 2025 study on post-operative instruction understanding and follow-up reported that 35.8% of patients experienced complications due to noncompliance; only 39.6% reported being informed about potential complications due to non-compliance—highlighting avoidable risk when education is incomplete.
Healthcare Worker Mental Health & Burnout (Why Reducing Operational Load Matters)
Burnout + Depression in Physicians (U.S. Federal Workforce Report): A 2024 U.S. health workforce report cited a 2024 survey where 49% of physicians reported burnout and 20% reported depression (improved from 2023 levels of 53% burnout and 23% depression).
Nursing Burnout Frequency (National Survey): The same report cites an NCSBN survey finding 45% of RNs and 45% of LPNs experience burnout at least a few times a week.
Burnout Trend Data at Scale (140 Medical Centers): A multi-year (2018–2023) workforce survey across 140 medical centers reported burnout rates ranging from 30.4% (2018) up to 39.8% (2022), with a partial decline to 35.4% in 2023; primary care physicians showed the highest burnout levels, reaching 57.6% in 2022.
Automation & Workload Reduction (Evidence It Can Ease Clinician Burden)
Ambient AI Scribe Use Reduced Burnout in 30 Days (Multicenter Study): A 2025 multicenter quality-improvement study found the proportion of clinicians experiencing burnout dropped from 51.9% to 38.8% after 30 days using an ambient AI scribe; it also improved note-related cognitive task load by 2.64 points (10-point scale) and reduced after-hours documentation time by 0.90 hours.
Randomized Trial (Two Ambient AI Scribes): A 2025 randomized clinical trial found one ambient AI scribe achieved a 9.5% decrease in time-in-note vs control; across any scribe use, Mini-Z scores improved by +2.76 points, task load decreased by –35.8 (0–400 scale), and work exhaustion decreased by –0.27 (0–4 scale).
EHR Burden Keeps Rising in Primary Care (2019–2023): A 2024 longitudinal study found average PCP time in the EHR per 8 hours of scheduled clinic increased by 28.4 minutes (7.8%), orders time increased by 58.9%, and patient medical advice message volume increased by 55.5%—a known burnout driver.
Team-Based Documentation Support Can Reduce EHR/Documentation Time: A 2024 national longitudinal cohort study found physicians adopting team-based documentation support experienced reduced documentation and EHR time (after a learning period), addressing the reality that physicians spend nearly half their day working in the EHR.
Related Links:
Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Surgical Patients’ Health Education - PMC
Post-discharge texting programme and associations with HCAHPS, readmissions, revisits - PubMed
BMJ Open (2024): Post-discharge texting programme outcomes
Impact of digital surgery scheduling systems on preoperative care: systematic review protocol - PMC
JMIR Perioperative Medicine (2024): Digital perioperative education/interventions
Group preoperative education before elective major surgery (2024 review) - ScienceDirect
Virtual Transition of Care Clinics and associated readmission rates - PubMed
Remote Patient Monitoring Platform after THA/TKA (ED odds, LOS) - PMC
Team-based digital communication RCT: phone calls reduced (2.3 → 0.5) - PMC
The Psychological Impact of Aesthetic Surgery: A Mini-Review
JMIR (2023): Telepsychiatry outcomes (PHQ-8/GAD-7 improvements)
Stress Reduction in Perioperative Care (2025): 17.12% fewer hospital days - PubMed
JAMA Network Open (2025): Smartphone-delivered digital CBT for GAD (RCT)
Average physician spends 50.7 months with unresolved malpractice claim - PubMed
Malpractice risk by specialty (7.4% claims/year; mean payment $274,887) - NEJM
Repeat-claim concentration (1% of physicians account for 32% of paid claims) - NEJM
CRICO Strategies (2015 PDF): 30% of 23,658 cases involved communication failure
AM Best: Medical Professional Liability Market (Webinar PDF)
AM Best (2025): MPL direct premiums written rose 5.4% to $13.02B in 2024
Washington OIC: 2023 Medical Malpractice Annual Report (loss + defense cost ratios)
WebAIM Million (2024): 95.9% detectable WCAG failures; 81% low contrast
UsableNet: ADA digital accessibility lawsuit tracker (4,187 in 2024)
Ophthalmology hospital webpages accessibility study (2024) - ScienceDirect
DOJ ADA: Effective Communication requirements
DOJ ADA: Web content accessibility rule fact sheet (WCAG references)
HHS OCR: Limited English Proficiency (Title VI language access)
HHS OCR: Title VI meaningful access guidance (LEP)
Canadian Human Rights Commission: About the Accessible Canada Act
Government of Canada: Guidance on Accessible Canada Regulations (alternate formats)
Accessibility Standards Canada: Communication guidance (accessible formats)
HBR/Bain: +5% retention can raise profits 25%–95%
BMJ Open (2025) PDF: Hospital discharge communication problems in 10 high-income nations
Annals of Internal Medicine (2003) PDF: Adverse events after discharge (19% within ~3 weeks)
JAMA Network Open (2025): Burnout Trends Among US Health Care Workers (2018–2023)
PMC Full Text: Burnout Trends Among US Health Care Workers (JAMA Network Open)
PMC (2024): EHR Workload Trends Among Academic Primary Care Physicians, 2019–2023
PMC (2024): Physician EHR Time Following Adoption of Team-Based Documentation Support
When you're ready to take your practice to the next level with state-of-the-art patient care, we're ready to bring you there
© 2025-2026 Easy Aftercare™, powered by Synchronous Technologies Group Inc. Patents pending.